What are the relationships between politics & the economy, culture & education within a country?
I. GENERAL INFORMATION
1. US politics
1.1. Government structure
The United States is a federal constitutional republic in which the federal government shares sovereignty with the state governments.
To ensure that no one branch of government would become too powerful, the Framers broke federal government up into three branches which are balanced and separate.
- Executive Branch: This is the presidential branch, with the President (Joe Biden) at its head who is elected by the entire country through the electoral college.
- Legislative Branch: This is the congressional branch, with both the House of Representatives and Senate.
- Judicial Branch: This is the courts branch with the Supreme Court (a panel of q judges or justices) at its head.
The point here is that each of the branches has the power to limit, or check, the other two and this creates a balance between the three separate powers.
Ex: The president (head of the executive branch) serves as commander in chief of the military forces, but Congress (legislative branch) appropriates funds for the military and votes to declare war. In addition, the Senate must ratify any peace treaties.
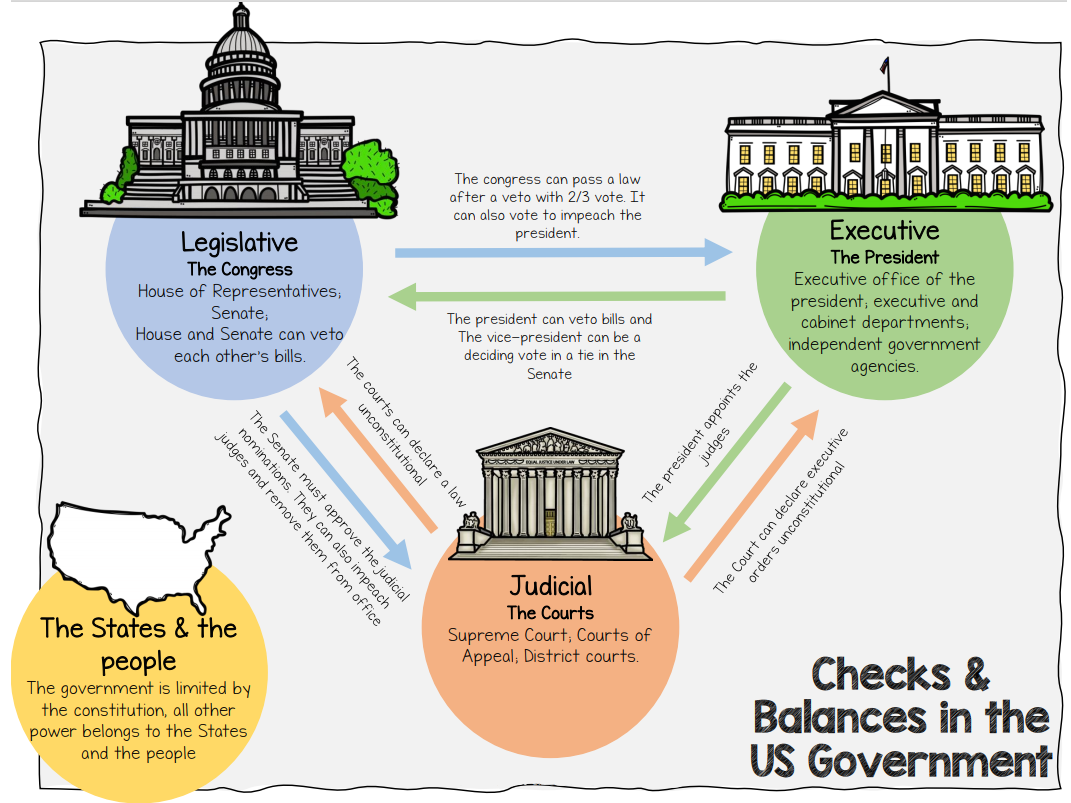
Figure 1: Checks & Balances in the US Government
1.2. Political system
1.2.1. Political parties and elections
• Political parties
Today, America is a multi-party system. The Democratic Party and the Republican Party dominate modern politics in the United States. Other parties, often generally termed “third parties”, in the U.S. include The Green Party, Libertarians, Constitution Party, Tea Party…

Figure 2: Political parties in the USA
The main difference between the two parties is, indeed, their political orientation. The Democratic Party is left-leaning, liberal and usually associated with progressiveness and equality. The Republican Party, instead, is right-leaning, traditional and associated with equity and economic freedom and with the ideal of “survival of the fittest”. Given their different origins and opposing political orientations, the two parties clash on a number of fundamental issues : tax, health care, abortion, labor and free trade,…..
Figure 3: Two major political parties in US
• US Presidential Election:
Americas distinctive nominating process is an additional structural barrier to third parties. In most nations, partisan nominations are controlled by the party organizations. But in the United States, it is the voters who make the ultimate determination of who the Republican and Democratic nominees will be. This system, of course, contributes to the fact that the United States has weaker formal party organizations than most other democracies.
- Election progress and requirements: The US Presidential Election takes place every four years. Candidates must be at least 35 years old, born in the United States and lived in the US for the previous 14 years to be eligible.
Presidential primaries and caucuses: votes for hopeful presidential candidates from each of the major parties.
Delegates: These delegates represent their state in the national party convention and vote to decide each party's presidential candidate.
National conventions (summer): to receive the nomination of the party
General Election campaigning: the presidential candidates go to rallies and take part in debates to win the support of voters across the nation. Moreover, they explain their plans and views to society.
Electoral College : On Election Day, voters go to the polling place and cast their vote for their preferred candidate. The voters elect their President and Vice President indirectly. Both are chosen by electors through the Electoral College process.
Inauguration Day : at the U.S. Capitol building in Washington D.C
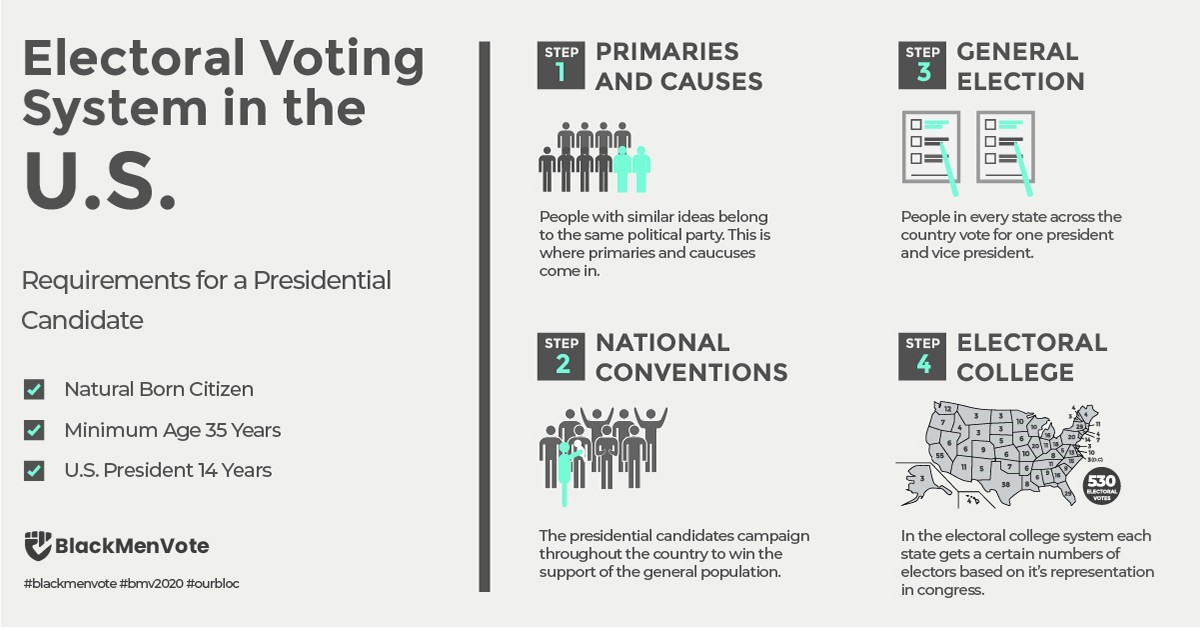
Figure 4: The U.S. electoral voting system
1.3. Voting behaviour
1.3.1. Voter turnout
The 2020 presidential election is over, the excitement and sense of urgency between both Republicans and Democrats seems to have reached new heights for this election cycle
In data from a recent Gallup survey, 77 percent of all U.S. registered voters said the outcome of this year’s presidential election matters more to them than in previous election years. That’s the highest percentage in the poll’s 26-year history, with the last five election cycles hovering around 70 percent.
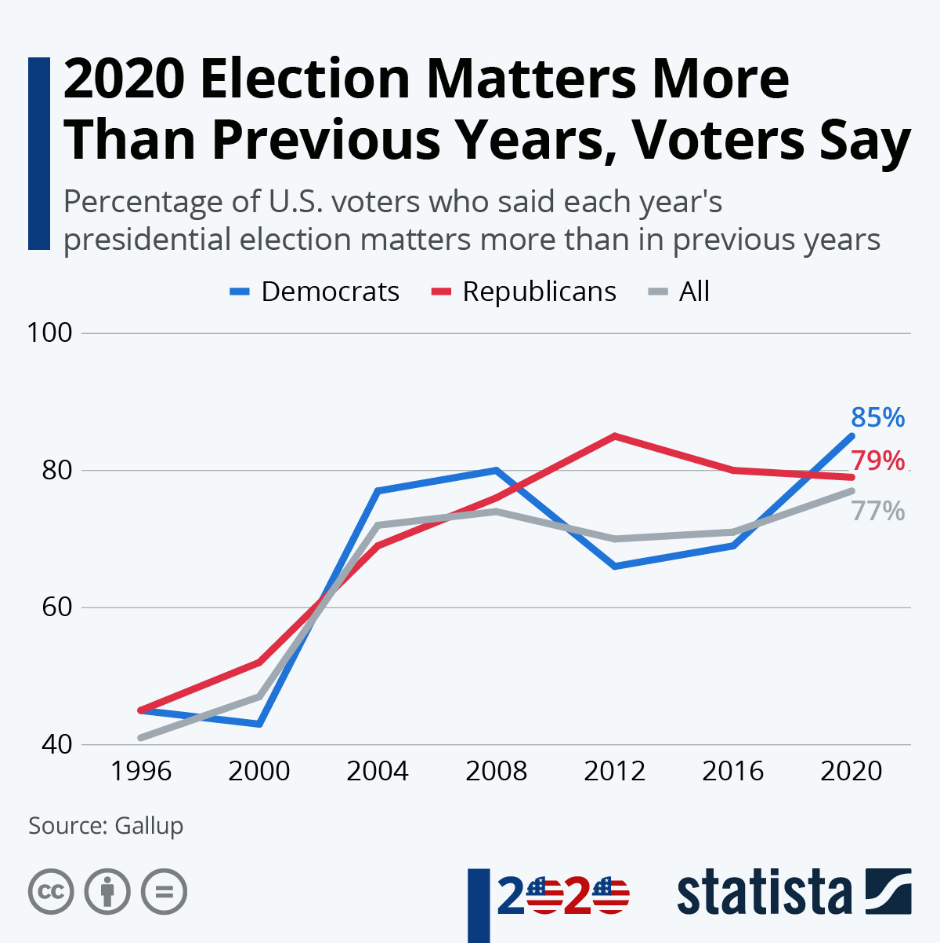
.
Figure 5: Voter turnout 2020
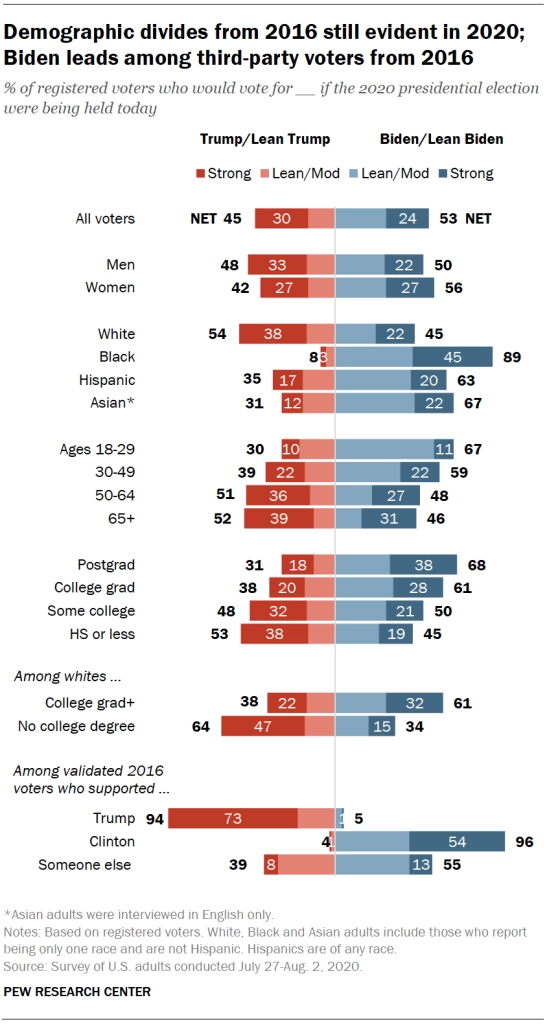
Voter turnout is the percentage of eligible voters who cast a ballot in an election. Socioeconomic factors such as education, income, gender, age ( reflects issues that people care about. Older people are more likely to vote than young people and are more likely to be politicians.) , and race significantly affect how likely individuals are to vote.
Figure 6: Voter turnout based on socioeconomic factors
Especially, media has a significant role for reaching youth and reports a massive and continuous increase in engagement during this election cycle. Although it’s too early to determine exact causation, NPR, in an October 29 article on surging youth turnout shared that the number of early voters under 30 who are voting for the first time in their life is more than double the number of first-time voters at this point in the 2016 election. and now every candidate has at least one Twitter profile and Facebook page
CLICK TO SEE MORE




 .
.